In the dynamic realm of manual and movement therapy, the concept of ‘treatment stacking’ has emerged as a game-changer. By intelligently combining various manual therapy modalities, we not only address musculoskeletal complaints more comprehensively but also tap into the fascinating realm of neuroscience, influencing the brain’s perception and response to threats.
Understanding Treatment Stacking: A Holistic Approach
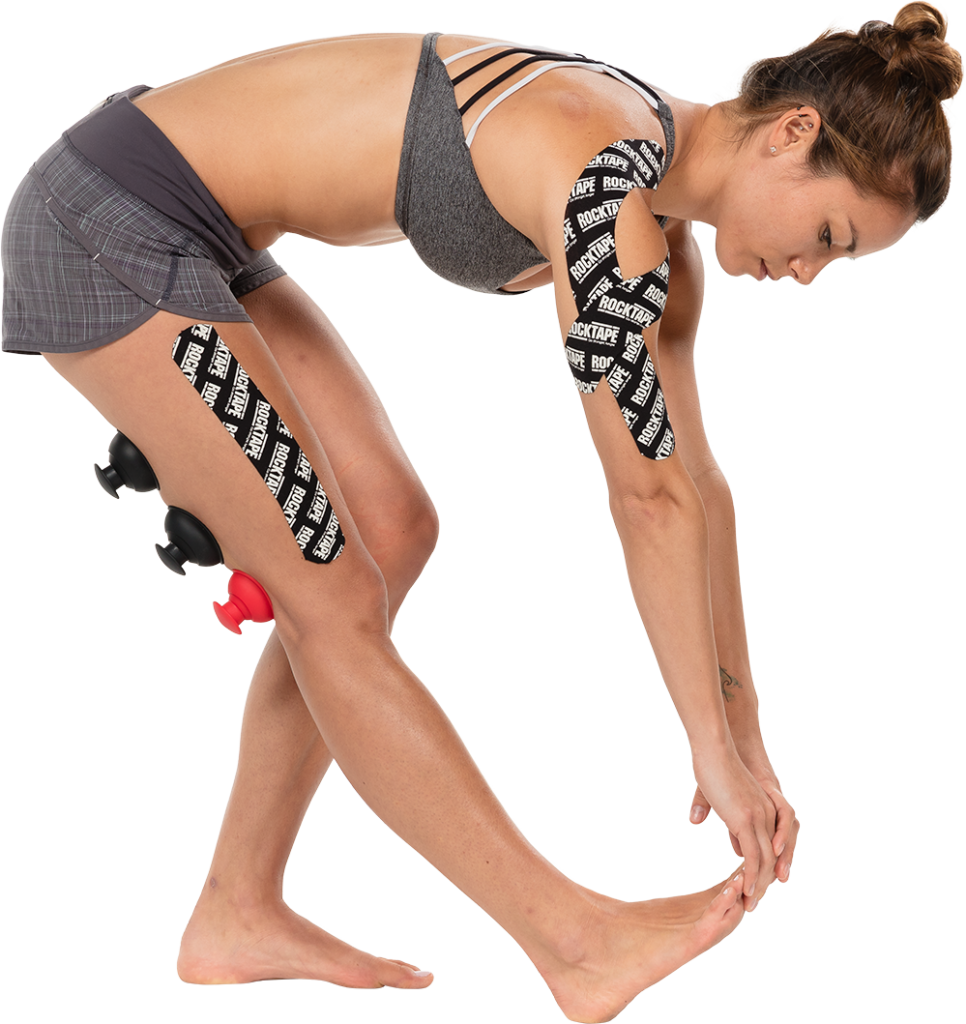
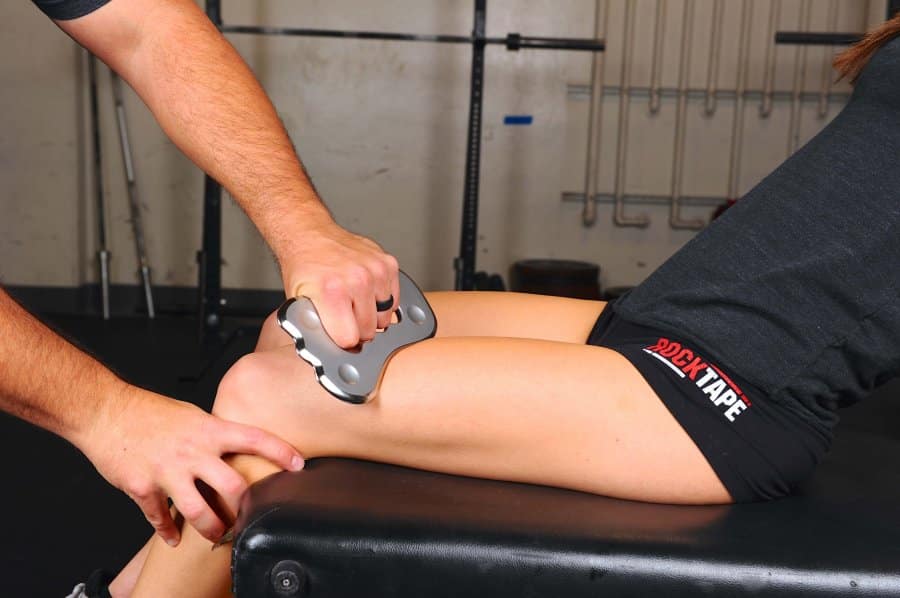
Musculoskeletal disorders often demand a multi-faceted approach. Treatment stacking involves strategically integrating diverse manual therapy tools such as Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Manipulation (IASTM), Myofascial Cupping, Compressional Floss Therapy, and Kinesiology Tape.

RockTape Treatment Stack
Science-Informed Tools: Beyond Mechanics
These tools transcend mere mechanical interventions. They become conduits for sensory stimulation, influencing the brain’s behavior in response to perceived threats. The ‘talk to the brain’ model, championed by the Functional Movement Training (FMT) education platform, underscores the importance of considering these interventions as a language that communicates with the brain.
Key Benefits of Treatment Stacking:
-
-
- Comprehensive Approach: Each modality contributes uniquely, addressing different aspects of the musculoskeletal issue. IASTM targets adhesions (densification), cupping enhances connective tissue gliding, floss therapy improves joint/soft tissue mobility, and kinesiology tape provides extended dynamic support to the tissues and communication to the nervous system.
- Neuroscience Integration: Understanding the neuroscience behind these tools transforms them from mechanical aids to communication tools. The brain plays a pivotal role in pain perception and motor control. Treatment stacking offers a comprehensive approach to influence the brain’s response, promoting neuroplasticity and adaptation. The ‘talk to the brain’ model serves as a guiding principle, emphasizing that introducing novel, non-noxious information to the brain enhances decision-making related to pain perception and movement quality.
- Enhanced Patient Outcomes: By leveraging a combination of modalities, therapists can tailor treatments to individual patient needs, leading to faster recovery and sustained results. An example would be with chronic lower back cases where treatment stacking proves crucial. Beyond traditional hands-on therapy, stacking various tools leverages therapeutic expectations, tapping into the placebo effect, and captivates the brain’s attention through the novelty of these interventions.
- Novel Sensory Stimulation: These modalities act as sensory stimuli, challenging the brain’s perception of threat and encouraging adaptive responses. This is especially crucial in chronic pain scenarios.
- The Role of Education: Continuous education proves indispensable. Staying abreast of the latest literature ensures clinicians remain at the forefront of proper tool utilization within the treatment stacking model. This commitment to learning reinforces the dynamic nature of manual and movement therapy. FMT’s educational framework empowers therapists to use these tools strategically and intentionally.
-
Stacking Approach:
Summary
In the evolving landscape of manual and movement therapy, treatment stacking stands as a testament to the integration of art and science. By delving into the nuances of these modalities and considering them as tools to converse with the brain, therapists can unlock new dimensions of patient care and elevate treatment outcomes to unprecedented levels.